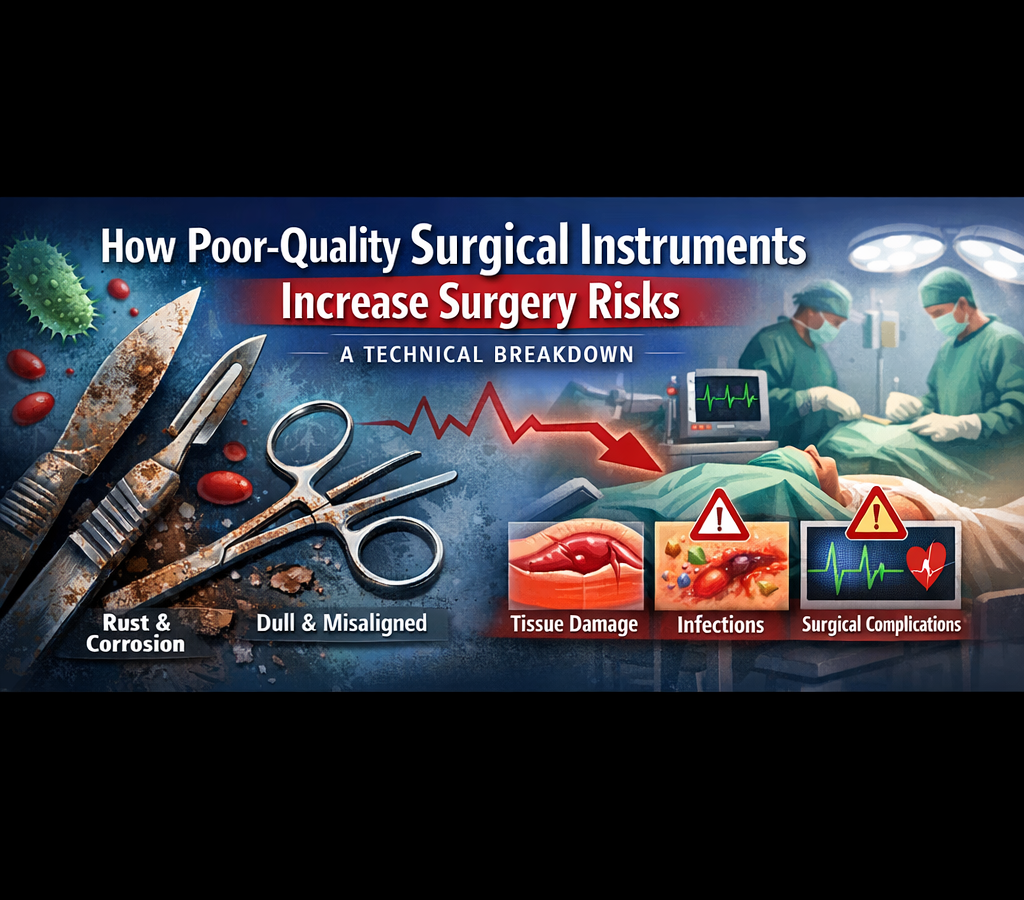
How Poor-Quality Surgical Instruments Increase Surgery Risks — A Technical Breakdown
Introduction
In modern surgery, precision is everything. While advanced techniques and skilled surgeons play a vital role, the quality of surgical instruments remains a critical — and often underestimated — factor in patient safety. Poor-quality surgical instruments can compromise surgical accuracy, increase infection risks, and even lead to life-threatening complications.
This technical breakdown explains how low-grade surgical instruments directly increase surgical risks, what causes these failures, and why investing in certified, high-quality instruments is essential for safe and successful procedures.
1. Material Failure: The Root of Most Instrument Problems
One of the most common issues with poor-quality surgical instruments is inferior material composition.
Low-grade stainless steel or improperly treated alloys can result in:
- Reduced tensile strength
- Metal fatigue
- Bending or warping during procedures
- Cracking or breakage under pressure
During surgery, even a minor material failure can cause tissue damage, procedural delays, or emergency instrument replacement — all of which increase patient risk.
2. Increased Risk of Infection Due to Surface Imperfections
High-quality surgical instruments feature smooth, non-porous surfaces. Poor-quality instruments often have:
- Micro-cracks
- Rough edges
- Inconsistent polishing
- Porous metal surfaces
These imperfections create ideal environments for bacterial growth and biofilm formation, making sterilization less effective. Even after autoclaving, bacteria may survive in microscopic crevices, significantly increasing the risk of post-operative infections.
3. Loss of Precision and Control
Surgical instruments are designed to function as extensions of the surgeon’s hands. Poor-quality tools compromise this relationship by causing:
- Misalignment in forceps and scissors
- Uneven blade edges
- Poor grip ergonomics
- Unstable spring mechanisms
As a result, surgeons experience reduced control, which can lead to:
- Inaccurate incisions
- Excessive tissue trauma
- Prolonged procedure time
Precision loss directly impacts surgical outcomes and patient recovery.
4. Rapid Dulling of Cutting Instruments
Scalpels, scissors, bone cutters, and dental instruments rely heavily on sharp, stable cutting edges. Inferior steel grades dull quickly due to:
- Low carbon content
- Improper heat treatment
- Weak edge retention
Dull instruments require additional force, increasing:
- Tissue damage
- Bleeding
- Surgeon fatigue
This not only affects surgical efficiency but also compromises healing and increases complication rates.
5. Corrosion and Rust After Sterilization
Repeated exposure to sterilization cycles — heat, pressure, moisture, and chemicals — tests the true quality of surgical steel.
Poor-quality instruments often develop:
- Rust spots
- Pitting corrosion
- Surface discoloration
Corrosion weakens the instrument structure and introduces contaminants, making the tool unsafe for continued use and increasing the risk of cross-contamination.
6. Mechanical Failure During Procedures
Low-quality manufacturing and poor quality control can lead to:
- Loose joints
- Weak hinges
- Faulty locking mechanisms
- Spring failure in needle holders or clamps
Mechanical failure during surgery can interrupt critical moments, force emergency tool changes, or result in incomplete procedures — all of which pose serious risks to patients.
7. Inconsistent Performance Across Instrument Sets
One of the biggest challenges with poor-quality instruments is inconsistency. Instruments from the same set may vary in:
- Hardness
- Sharpness
- Alignment
- Weight balance
This unpredictability prevents surgeons from developing reliable muscle memory, increasing the likelihood of errors during delicate procedures.
8. Increased Long-Term Costs for Healthcare Facilities
Although low-quality instruments appear cheaper upfront, they result in:
- Frequent replacements
- Higher maintenance costs
- Increased sterilization failures
- Greater liability risks
Hospitals and clinics often spend significantly more over time replacing inferior tools compared to investing in durable, high-quality instruments from the start.
9. Compliance & Regulatory Risks
Medical facilities are required to follow strict regulations regarding surgical equipment. Poor-quality instruments may:
- Fail CE, ISO, or FDA compliance
- Lack proper documentation
- Create audit and legal risks
Using non-compliant instruments can damage institutional reputation and lead to serious legal consequences.
10. How to Avoid These Risks
To reduce surgical risks, always choose instruments that offer:
- Certified stainless steel (e.g., German-grade)
- CE and ISO compliance
- Smooth, non-porous finishes
- Verified manufacturer traceability
- Consistent quality control
Partnering with reputable manufacturers ensures reliability, safety, and long-term performance.
Why Quality Matters at Soltech Medical
At Soltech Medical, we manufacture surgical and dental instruments using premium-grade stainless steel and strict quality control protocols. Our instruments are designed to deliver:
- Precision and durability
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Reliable sterilization compatibility
- Consistent performance across every set
Each instrument undergoes inspection to ensure it meets international medical standards before reaching our clients.
Conclusion
Poor-quality surgical instruments don’t just affect efficiency — they increase surgical risks, compromise patient safety, and raise long-term costs. From material failure and infection risks to mechanical breakdowns, the consequences are serious and avoidable.
Investing in high-quality, certified surgical instruments is not optional — it’s a responsibility. Choosing the right instruments protects surgeons, patients, and healthcare institutions alike.