How Surgical Instruments Are Tested Before Clinical Use
Introduction
Before a surgical instrument ever reaches an operating room, it must pass a series of strict tests designed to ensure safety, precision, durability, and compliance. These tests are essential because even the smallest defect can lead to surgical complications, infections, or instrument failure during critical procedures.
In this article, we provide a technical breakdown of how surgical instruments are tested before clinical use, and why these testing processes are crucial for patient safety and surgical success.
Why Testing Surgical Instruments Is Critical
Surgical instruments are exposed to extreme conditions, including:
- High mechanical stress
- Repeated sterilization cycles
- Direct contact with tissue and bodily fluids
Testing ensures that instruments:
- Perform reliably during procedures
- Maintain structural integrity
- Remain safe after repeated use and sterilization
- Comply with international medical standards
Without proper testing, instruments can fail when they are needed most.
1. Raw Material Inspection
Testing begins before manufacturing even starts.
What Is Tested
- Stainless steel grade (e.g., 420, 440A, 304)
- Chemical composition
- Carbon content
- Corrosion resistance
Why It Matters
Using the wrong alloy or poor-quality steel can lead to rust, breakage, or rapid dulling. Only medical-grade stainless steel is approved for surgical use.
2. Dimensional & Visual Inspection
After forging and machining, instruments are carefully examined.
Key Checks Include
- Accurate dimensions and alignment
- Proper jaw closure in forceps
- Symmetry of cutting edges
- Smooth surface finish
Even slight misalignment can affect surgical precision.
3. Hardness & Strength Testing
Mechanical strength is essential for surgical instruments that must withstand force without bending or breaking.
Common Tests
- Rockwell or Vickers hardness tests
- Tensile strength testing
- Flexibility and stress resistance evaluation
These tests ensure the instrument can handle surgical pressure safely.
4. Functional Performance Testing
Every instrument must perform exactly as intended.
Examples
- Scissors are tested for smooth cutting and edge retention
- Needle holders are tested for grip strength
- Forceps are checked for secure locking mechanisms
- Hinges and joints are tested for smooth movement
Functional testing ensures reliability during real surgical conditions.
5. Surface Finish & Polishing Inspection
Surface quality directly affects sterilization and infection control.
What Is Evaluated
- Smoothness of polish
- Absence of micro-cracks or pores
- No sharp edges or burrs
A non-porous surface prevents bacterial buildup and improves sterilization efficiency.
6. Corrosion Resistance Testing
Surgical instruments must resist rust even after repeated sterilization.
Testing Methods
- Exposure to moisture and chemicals
- Simulated sterilization cycles
- Salt spray or humidity tests
Corrosion resistance testing ensures instruments remain safe over long-term use.
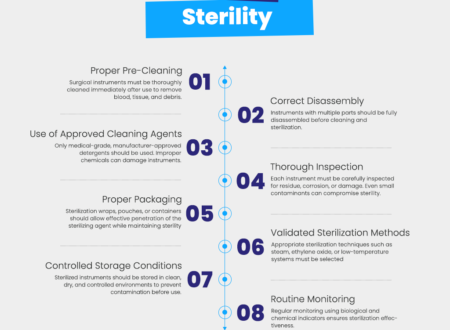
7. Sterilization Compatibility Testing
Instruments must withstand repeated sterilization without degradation.
Sterilization Methods Tested
- Steam autoclaving
- Chemical sterilization
- High-temperature exposure
Testing confirms that instruments do not warp, corrode, or lose sharpness after sterilization.
8. Mechanical Fatigue Testing
Reusable instruments undergo repeated opening, closing, cutting, or clamping.
Why This Test Matters
- Detects hinge failure
- Identifies weak locking mechanisms
- Ensures long-term durability
Mechanical fatigue testing simulates years of clinical use.
9. Final Quality Control Inspection
Before packaging, instruments undergo a final inspection.
Final Checks Include
- Overall functionality
- Cleanliness
- Packaging integrity
- Labeling and batch numbers
- Compliance markings (CE, ISO, GMP)
Only instruments that pass every inspection stage are approved for shipment.
10. Compliance with International Standards
Testing processes align with international medical standards such as:
- ISO 13485 (Medical device quality management)
- CE marking (European regulatory compliance)
- GMP guidelines (Manufacturing best practices)
Compliance ensures global acceptance and clinical safety.
Why Testing Matters at Soltech Medical
At Soltech Medical, every surgical and dental instrument undergoes a rigorous multi-stage testing process. From raw material inspection to final quality control, our focus is on:
- Precision manufacturing
- Consistent performance
- High corrosion resistance
- Sterilization safety
- Compliance with international standards
Our testing protocols ensure instruments perform reliably in real surgical environments.